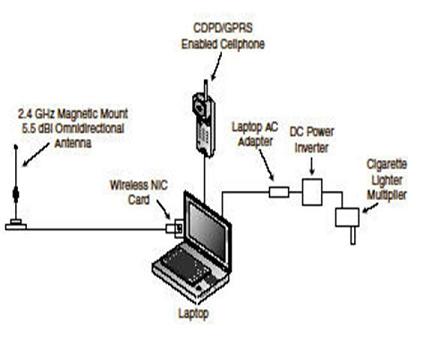
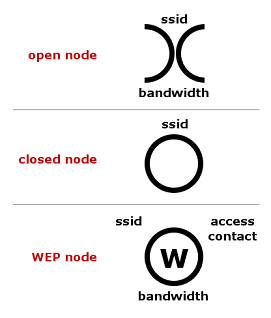
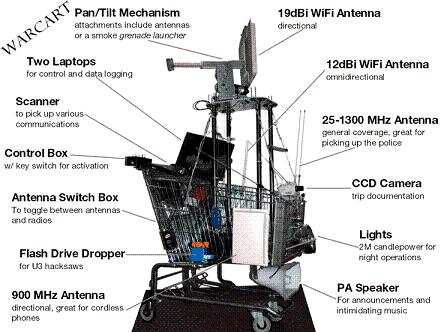
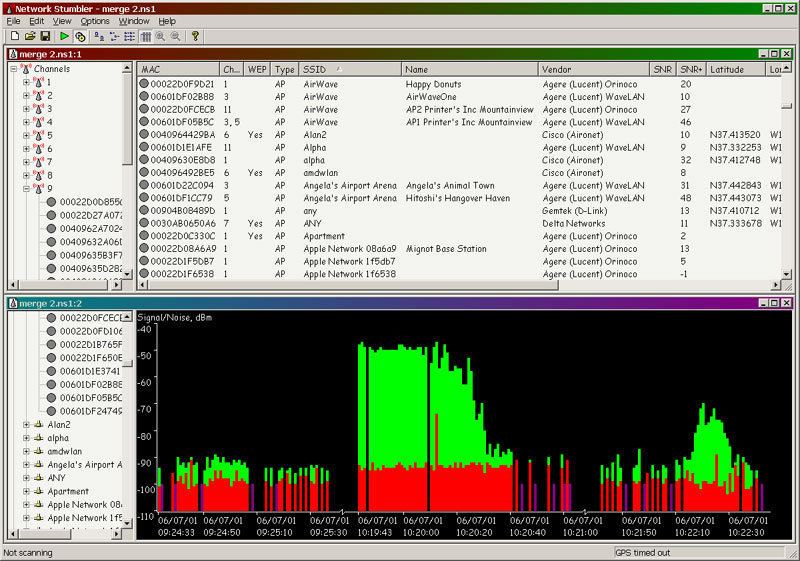
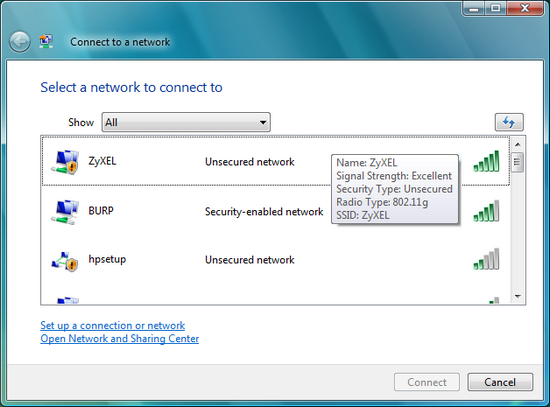
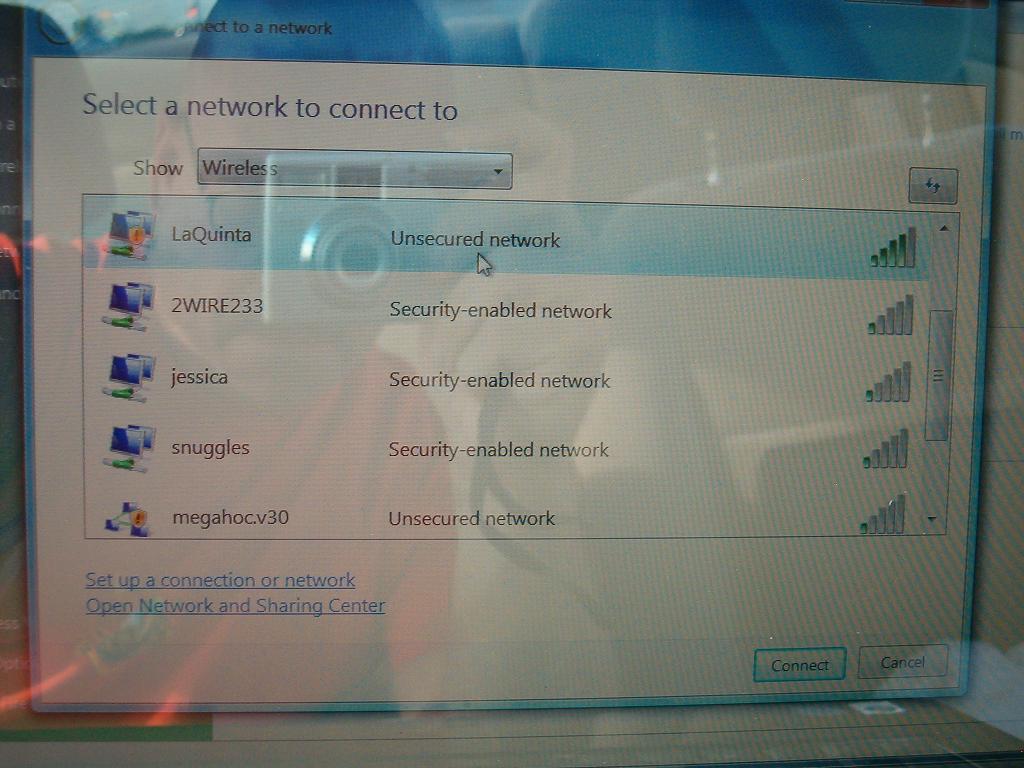
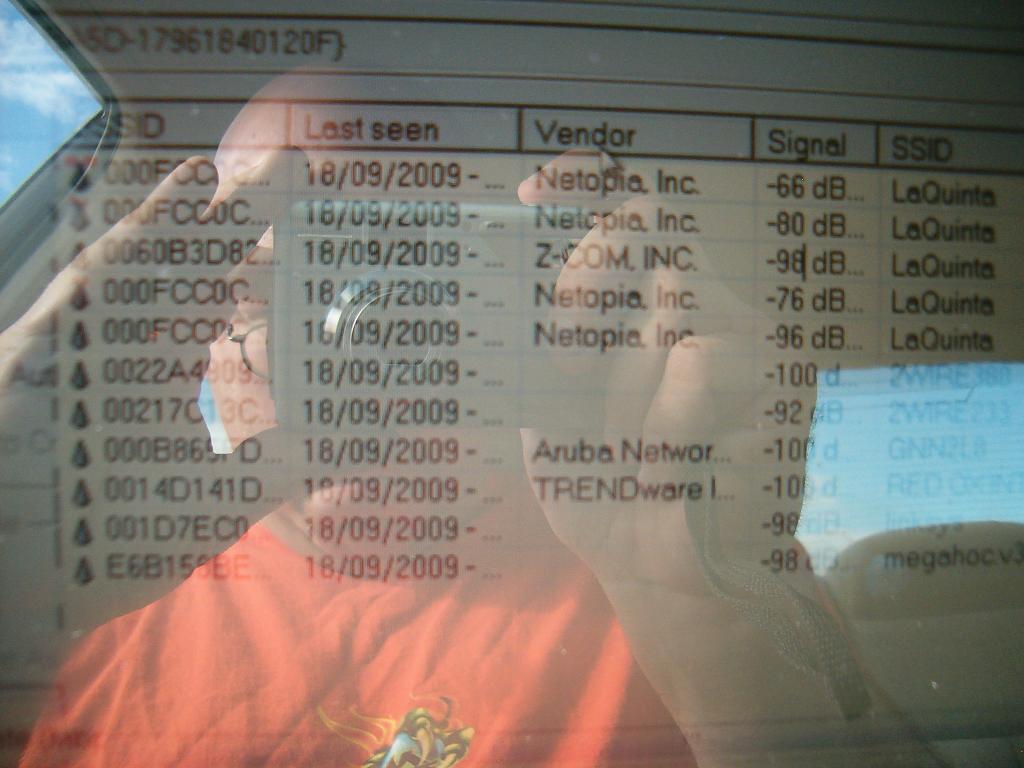
So far all you have done is picked up RF signals out in the public airwaves and logged them to your computer. This is not a crime. The next thing - Attaching to the network is.
A Wireless Access Point (AP) is the central bridge device used in an Infrastructure (as opposed to Ad Hoc) wireless network. (See Wi-Fi Network Types) Traffic from the wireless side of the bridge is sent to the Ethernet (wired) side of the bridge, and vice versa. The wireless access point controls all traffic with wireless client radios.
Note: A wireless router, which is often less expensive than a wireless access point, can be configured to work as just a wireless access point -- see Wi-Fi How To Use a wireless router as a wireless access point.
Wireless Router
A wireless router typically consists of three parts:
1.Ethernet router, including:
DHCP client and server
NAT(PAT)
Firewall
2. Owner Interface (usually web interface)
3.Wireless access point hardware (radio)
Some boxes also include either: DSL modem orCable modem.
MAC Address
MAC stands for Media Access Control and the MAC address is a computer's true name on a LAN. An Ethernet MAC address is a six byte number, usually expressed as a twelve digit hexadecimal number ( 1AB4C234AB1F).
IPs are translated to MAC address by a protocol called ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). A computer with and IP of 192.168.1.1 wants to send information to another computer on the LAN that has an IP of 192.168.1.50 . The computer with 192.168.1.1 will send out a broadcast to all stations on the LAN asking who has the IP 192.168.1.50? Then the box that has 192.168.1.50 will respond to 192.168.1.1 with it's MAC address which is cached in 192.168.1.1's ARP table.
Spoofing MAC is important for the wardriver,
1. To hide your real machine's ID
2. To sniff traffic meant for the real computer with that MAC
3. To bypass router security that is set to only allow certain machine's MACs
4. To take over communication between machines that have already authenicated with each other to by pass a login.
Wardriving - get attached
Your laptop and wifi AP need to do their handshake to authenticate to each other. The usual TCP/IP rules apply here, one computer says "Hi I am Wardriver with MAC de.43.sf.3.f.e" the other computer says "Ok, I am Wifi router MAC ew.3d.fE.54, Welcome" the one says "Thanks!" All this can happen to computers and phones that are set to locate any wifi signal and attach - this is bad if you set up a rogue AP. This takes about less than a minute, but you have to maintain signal strength by staying near the AP.
PnP of Wifi
The wifi AP was meant to be PnP friendly - Plug and Play. It allows wifi device to locate it by its broadcast (SSID) and it has automatic login capabilities. A poorly configured laptop can attach to a unsecured wifi AP only because it has the best signal strength - not because it is allowed to. This can be used as an excuse for using someone else's wifi AP - your neighbor's wifi AP could be closer to your TV room than yours is downstairs. The same can happen for your neighbor using your wifi AP.
There are also some wifi AP that were meant to be provided for paying customers of a hotel, cafe, or bookstore - sitting outside and surping their wifi would not be kosher. Some wifi AP are setup for corporate or business use, but it was poorly configured because the sysadmin didn't want to configure all the machines that will access it. So again - just because you can attach to a AP, you are still responsible for determining if the laws are being broken!
Association and Authenication
All the APs transmit Beacon frames a few times each second that contain the SSID, time, capabilities, supported rates, and channel. wifi users can chose to associate with an AP based on the signal strength of each AP.
The association is a two-step process. A wifi user that is unauthenticated and unassociated listens for Beacon frames. The wifi user selects a AP to join. The wifi user and the AP mutually authenticate themselves by exchanging Authentication management frames. The client is now authenticated, but unassociated. In the second step, the station sends an Association Request frame, to which the AP responds with an Association Response frame that includes an Association ID to the station. The station is now authenticated and associated.
Authentication is the process of proving identity of a station to another station or AP. In the open system authentication, all stations are authenticated without any checking. In the closed network architecture, the stations must know the SSID of the AP in order to connect to the AP. The shared key authentication uses a standard challenge and response along with a shared secret key. A station can be authenticated with several APs at the same time, but associated with one AP at a time.
The so-called promiscuous mode allows the capture of all wireless packets of an associated network. In this mode, packets cannot be read until authentication and association are completed.
Lastly, just because you are authenticated to a wifi AP, you may still need to authenticate to regular network Domain logins.
Wardriver for Free Internet
Windows network discovery of the wifi AP will discover the gateway and DNS IPs so it can access the internet. Your browser will confirm. Surf away. Just be aware that this unsecured wifi AP means that sensitive stuff like your real email login, bank account login, should not be trusted on the network. The AP can log your MAC and where you go, the network can have more logs, again logging your laptops fingerprint (MAC, OS, version, Browser type, version, machine type) and what URLs and files you requested.
The Dark side of Wardriving
Welcome to the Dark Side of Wardriving because now you want more than internet right? - after you attach to the wifi AP, why not discover the other devices on the same AP or network? You can use a IP scanner or a sniffer. The IP scanner you would scan within the IP block you are in - 192.169.1.0 through 192.168.1.255 for example.
This will show all the other devices that are attached to the wifi AP - cameras, printers, desktops, laptops, iphones, and routers.
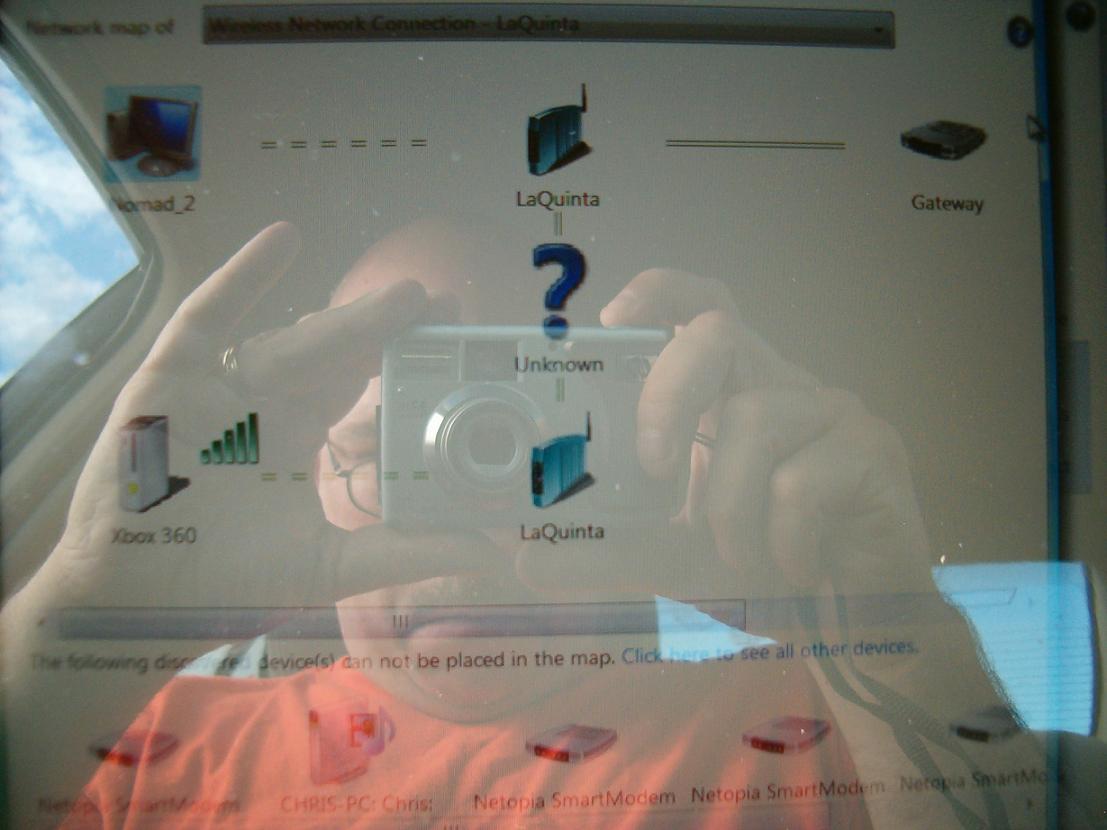 WAPJacking - Wireless Access Point Hijacking
WAPJacking - Wireless Access Point Hijacking
Once you have access to the wifi AP webinterface you can change the settings. The terminology I saw for this was WAPJacking - you take over the wifi AP by locking out the owner (as long as everything works, they don't check anyways) You can change the DNS and Gateway to a malicious machine to perform man-in-the-middle attacks or sniffing. Phishing by this method works very well as the owner will input the sensitive information when he makes a normal visit to the website, not a funny email link. This is hijacking the ownership of the wifi AP, and requires no special tools or special skills - you use the default IP and factory login to gain control of a unsecured wifi AP. If you have been locked out of your wifi AP, you can hit a recessed reset button on the back of the device, and it will reboot to the orginal factory settings. Simply changing the default user login can prevent this.
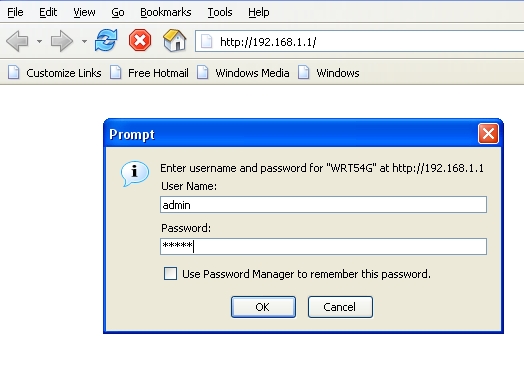
Always carry or memorize the
default wifi AP webinterface specs This is the default IP the wifi AP router is on, the default SSID, and the default user and password. While you can find extensive lists of default logins on the internet, here is a short one for wifi APs - notice similarities in the IP range - this follows the internet rules of using IPs for small networks. Medium to large sized networks can change this IP to 172.xx.xx.xx to 10.10.xx.xx, the 192.168.xx.xx. IP range tells you that it is likely a small residental or small business wifi AP.
You can also search the internet for owner's manuals or guides for the wifi AP, they are hosted on manufacturer websites and will tell you everything about that router. Third party sites about networking can host default password list
http://www.cirt.net/passwords
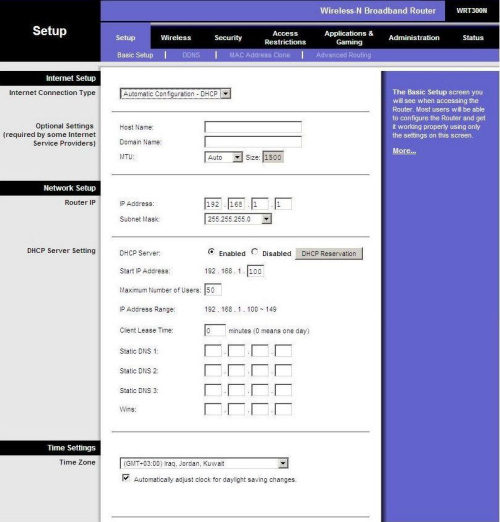 WarKitting
WarKitting
Since you have access to the webinterface, take it to a higher level - you can have the router upload modified firmware. Warkit is a rootkit for the wifi AP, you will have to find various coders or forums that can decode a wifi AP's firmware and code in your malware. This is a kernal level hack and makes it harder to detect - owners can access the webinterface and never know that the rootkit is hiding things from them. They can use the reset button, and the modified firmware will just be reloaded.
Uploading firmware is easy
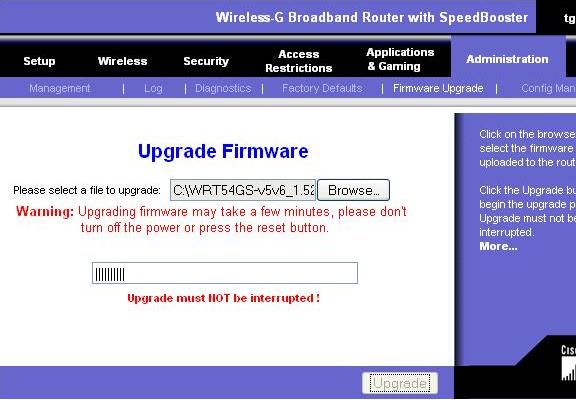
--
Brick and Run or Phlashing
Brick and Run is a tactic used on smaller networks - on small networks the router is the only one that will have usable logs to detect a intruder. The ISP can log this stuff on you, the fingerprint of your laptop, the MAC, and where you went. You are doing this to cover your tracks at the ISP customer level. Brick and Run is flashing the firmware of the wifi AP to erase your tracks. You would upload the firmware and the wifi AP will reboot automatically - you leave during this process and the wifi AP will reboot with no trace of you. This requires coding of the firmware to keep the old wifi AP settings as not to tip off the owner. Lacking the properly coded firmware - you would upload a corrupt file - this will cause the wifi AP to reboot and become useless! If the owner is unable to access the wifi AP interface to view the logs - it worked! But, the ultimate goal is to reflash so the wifi AP keeps on working.
Network attacks
 Session Hijacking
Session Hijacking
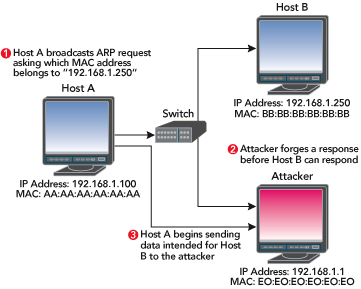
Once on a local network you can perform a session hijacking of a authenicated user logged in to a server. The user has an on-going connection with a server which he has used a login to authenicate. Hijacking occurs when an attacker causes the user to lose his connection, and the attacker assumes his identity and privileges for the connection to the server. The attacker disables temporarily the user’s system, say by a DoS attack or a buffer overflow exploit. The attacker now has all the access that the user has. When he is done, he stops the DoS attack, and lets the user resume. The user may not detect the interruption if the disruption lasts no more than a couple of seconds. Hijacking can be achieved by using forged Disassociation DoS attack and forged packets that have the victim's IP and MAC address. Corporate wireless networks are often set up so that the user is directed to an authentication server when his station attempts a connection with an AP - this is for the network logon. The network logon can be merely having the same IP and MAC address as one of the local machines, or an actual user/pass. The corporate network logon can be for cafe wifi hotspots or hotels and are not hard to crack.
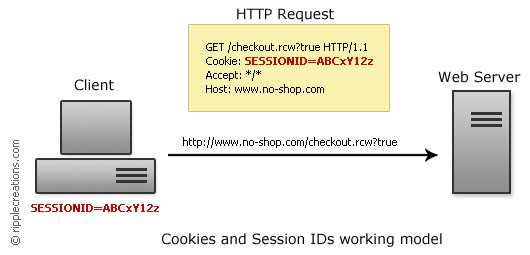
Session-Riding with sniffed cookies
 ARP Poisoning
ARP Poisoning
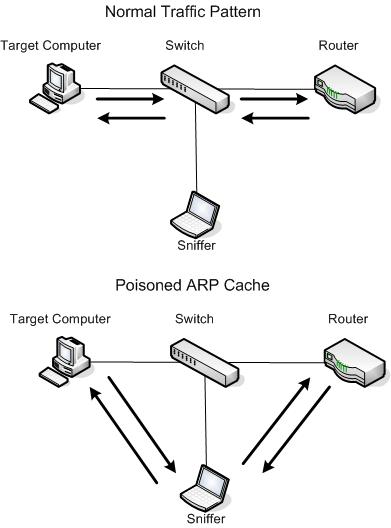
ARP poisoning technique is possible with APs that are connected to a switch/hub along with other wired clients.
ARP is used to determine the MAC address of a device whose IP address is known. The translation is performed with a table look-up - this can be on the wifi router or your machine. The ARP cache accumulates to build the network profile of users. If the ARP cache does not have an entry for an IP address, the outgoing IP packet is queued, and an ARP Request packet sent out that requests “If you are "IP address" then tell me your Ethernet address is” . The host with the target IP is expected to respond with an ARP Reply, which contains the MAC address of the host. Once the table is updated because of receiving this response, all the queued IP packets can now be sent.
This ARP poison flaw works because the ARP does not provide for any verification that the responses are from valid hosts! This corrupts the ARP cache that the OS maintains with wrong MAC addresses for some IP addresses. An attacker accomplishes this by sending an ARP Reply packet that is deliberately constructed with a “wrong” MAC address. Because ARP is a stateless protocol, a machine receiving an ARP Reply cannot determine if the response is due to a request it sent or not!
ARP poisoning is one of the techniques that enables the man-in-the-middle attack. An attacker on machine X inserts himself between two hosts B and C by (i) poisoning B so that C’s IP address is associated with X’s MAC address, (ii) poisoning C so that B’s address is associated with X’s MAC address, and (iii) relaying the packets X receives.
The ARP poison attack is applicable to all hosts in a subnet. Most APs act as transparent MAC layer bridges, and so all stations associated with it are vulnerable. If an access point is connected directly to a hub or a switch without an intervening router/firewall, then all hosts connected to that hub or switch are susceptible. Making home and small business networking easy for users have created devices that combine a network switch with four or five ports, an AP, a router and a DSL/cable modem connecting to the Internet at large. Internally, the AP is connected to the switch. As a result, an attacker on a wireless station can become a M-I-T-M between two wired hosts, one wired one wireless, or both wireless hosts.
Wifi Denial of Service
A denial of service (DoS) occurs when a system is not providing services to authorized clients because of resource exhaustion or a special packets that disconnect the client from the AP. DoS attacks are difficult to prevent on wifi networks and difficult to stop an on-going attack, and the victim might not even detect the attacks. The duration of such DoS may range from milliseconds to hours. A DoS attack against an individual station is mainly for session hijacking.
DoS by Jamming
Consumer appliances such as microwave ovens, baby monitors, and cordless phones operate on the unregulated 2.4GHz radio frequency. You can also by kits to assemble a electronic jammer. The attacker can unleash large amounts of noise using these devices and jam the airwaves so that the signal to noise drops too low for the machines to accept them. Jamming signals is illegal by FCC codes that require devices not to interfere with each other.
DoS by Associations
The AP stores data supplied by the connect computers in the Association Request into a table called the Association Table that the AP maintains in its memory. When this table overflows, the AP would refuse further clients. The actual size of this table varies among different models of APs.
IEEE 802.11 specifies a maximum value of 2007 concurrent associations to an AP. The attacker authenticates several non-existing stations using legitimate-looking but randomly generated MAC addresses. The attacker then sends a flood of spoofed associate requests so that the association table overflows. Once the table has reached its limit - no other users will be able to connect to the wifi AP. Enabling MAC filtering in the AP will prevent this attack as it require the MAC to approved by the sysadmin.
DoS by Forged Dissociation
The attacker sends a spoofed Disassociation frame to a victim's computer where the source MAC address is set to that of the AP.
This opens a session hijacking by allowing the attacker to reassociate as the victim to the wifi AP - the victim's computer is still authenticated but needs only to reassociate with the wifi AP. It does this by sending a Reassociation Requests to the AP. The AP may send a Reassociation Response accepting the attacker's machine spoofing as the victim's machine and the station can then resume sending data. Meanwhile the attacker keeps sending frames that deauthenticates the victim's machine from the AP.
DoS by Forged Deauthentication
The attacker sends a spoofed Deauthentication frame where the source MAC address is spoofed to that of the AP. The victim's computer is now unassociated and unauthenticated, from the wifi AP. The victim will have to reconnect. To prevent a reconnection, the attacker continues to send Deauthentication frames for a desired period.
The mischievous packets of Disassociation and Deauthentication are sent directly to the client, so these will not be logged by the AP or IDS, and neither MAC filtering nor WEP protection will prevent it.
--
Wardriver Tools
Windows already has its own network discovery tools and wlan tools included in Professional versions. Serious hackers and network auditors use the open-source operating system Linux as the platform from which they launch attacks and perform analysis - this is because other companies charge money for applications to do this, open source means people can share or make it freeware. Windows does not make it easy for freeware coders to write code for it, the market for wardriving tools is strict due to legal implications. These tools can work on several OS, Windows, Mac and Linux, but it might require a certain wifi adaptor. This is not a comprehensive list, but shows the range of tools.
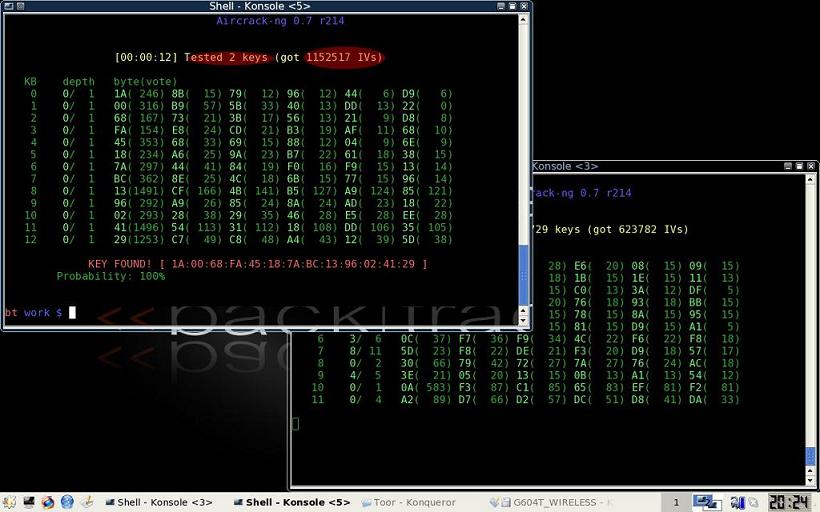
Aircrack
Aircrack/Aircrack-ng is also available on the Windows platform, albeit without the packet injection capabilities offered by aireplay. They come with the following tools:
airmon.sh - a utility to check an interfaces status and placing the interface into monitor mode
airodump - 802.11 packet capture program (the resulting captures are used with aircrack)
aircrack - static WEP and WPA-PSK key cracker that uses airodump captures as its input
aireplay - 802.11 packet injection program *Does not support Orinoco drivers
airdecap - decrypts WEP/WPA capture files
arpforge - tool for forging ARP request packets
 AirJack
AirJack
(802.11ninja.net/airjack/) is a collection of wireless card drivers and related programs. It includes a program called monkey_jack that automates the MITM attack. Wlan_jack is a DoS tool that accepts a target source and BSSID to send continuous deauthenticate frames to a single client or an entire network (broadcast address). Essid_jack sends a disassociate frame to a target client in order to force the client to reassociate with the network, thereby giving up the network SSID.
AirSnort
AirSnort is a wireless LAN (WLAN) tool which recovers encryption keys." AirSnort operates by passively monitoring transmissions, computing the encryption key when enough packets have been gathered. In even more simplistic terms, AirSnort is a program that listens to the wireless radio transmissions of a network and gathers them into a meaningful manner. After enough time has passed (sometimes in a matter of hours) and data are gathered, analytical tools process the data until the network security is broken. At that point everything that crosses the network can be read in plain text. (
www.airsnort.shmoo.com )
AirSnarf
AirSnarf is an access point spoofing tool based off the simplest way to dupe users into handing over their sensitive information to rouge hackers. Quite simply this application mimics a legitimate access point. The method of attack is broken down into recreating an identical logon webpage that would normally be displayed by the AP. The user is bumped off the network and forced to re-login or is caught before they login the first time. The simple trick convinces them into voluntary sending their login information to the hacker who can then use it at their disposal. It is extremely simple yet effective. All the details of the AP connection are legitimate to the unsuspecting user within their network configuration. They never realize this has happened in some cases as you then authenticate them to the network and allow them to pass through your computer.
APTools
APTools is a utility that queries ARP Tables and Content-Addressable Memory (CAM) for MAC Address ranges associated with 802.11b Access Points. It will also utilize Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP)
http://winfingerprint.sourceforge.net/aptools.php
AP Hunter
AP Hunter (Access Point Hunter) can find and automatically connect to whatever wireless network is within range. AP Hunter can be used for site surveys, writing the results in a file.
Airpwn
Airpwn is a tool for generic packet injection on an 802.11 network.
airpwn requires two 802.11b interfaces, one for listening, and another for injecting. It uses a config file with multiple config sections to respond to specific data packets with arbitrary content.
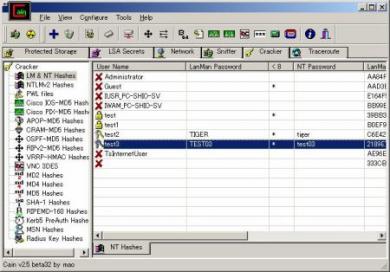
Cain & Abel
This tool can be used for sniffing and attacks to a wifi ARP. The tool can also be used to enumerate windows machines on the local network. VOIP cracking available.
 Madwifi
http://sourceforge.net/projects/madwifi/ http://madwifi.org/
Madwifi
http://sourceforge.net/projects/madwifi/ http://madwifi.org/
Multiband Atheros Driver for WiFi (MADWIFI): Linux driver for 802.11a/b/g universal NIC cards - Cardbus, PCI, or miniPCI - using Atheros chip sets.
MadMAC
MadMACs: MAC Address Spoofing And Host Name Randomizing App For Windows.
http://www.irongeek.com/i.php?page=secu ... ac-spoofer. Can work with Vista.
Ettercap
Ettercap (
http://ettercap.sourceforge.net) is capable of performing ARP poisoning as well as Cain & Abel. Linux, Mac OS, and Windows
http://ettercap.sourceforge.net/download.php
WEPcrack
WEPcrack, simultaneously being developed along with AirSnort, is another wireless network cracking tool. It too exploits the vulnerabilities in the RC4 Algorithm, which comprise the WEP security parameters. While WEPcrack is a complete cracking tool, it is actually comprised of three different hacking applications all of which are based on the development language of PERL. The first, WeakIVGen, allows a user to emulate the encryption output of 802.11 networks to weaken the secret key used to encrypt the network traffic. Prism-getIV is the second application that will analyze packets of information until ultimately matching patterns to the one known to decrypt the secret key. Thirdly the WEPcrack application pulls the two other beneficial data outputs together to decipher the network encryption. (
www.wepcrack.sourceforge.net)
WEPWedgie
WEPWedgie is a toolkit for determining 802.11 WEP keystreams and injecting traffic with known keystreams. The toolkit also includes logic for firewall rule mapping, pingscanning, and portscanning via the injection channel and a cellular modem htp://sourceforge.net/projects/wepwedgie/
WEPattack
WepAttack is a WLAN open source Linux tool for breaking 802.11 WEP keys. This tool is based on an active dictionary attack that tests millions of words to find the right key. Only one packet is required to start an attack. htp://wepattack.sourceforge.net/
LORCON
Loss Of Radio Connectivity
http://802.11ninja.net/lorcon/ - Linux -
The LORCON packet injection library provides a high level interface to transmit IEEE 802.11 packets onto a wireless medium. Written for Linux systems, this architecture simplifies the development of 802.11 packet injection through an abstraction layer, making the development of auditing and assessment tools driver- independent.
Wifitap
WifiTap allows users to connect to wifi networks using traffic injection. The concept is the same as most "man-in-the-middle" attacks. For WifiTap to work, another system must have an association with an access point that the WifiTap system wants to pass traffic through. The system running wifitap is not associated with any wireless access point and the system is not handled by any access point.
http://sid.rstack.org/static/articles/w ... fitap.html
Kismet
Kismet is an extremely useful tool that supports more of an intrusion detection approach to the wireless security. However, Kismet can be used to detect and analyze access points within range of the computer on which it is installed. Among many other things, the software will report the SSID of the access point, whether or not it is using WEP, which channels are being used, and the range of IP addresses employed. Other useful features of Kismet include de-cloaking of hidden wireless networks, and graphical mapping of networks using GPS integration.
Ethereal - Now Wireshark
Ethereal/Wireshark is a pre-production network capturing utility. Wireshark is the newer version of Ethereal, Ethereal older versions can still run on todays machines. It is capable of identifying and analyzing 530 different network protocols, Ethereal can pose a substantial threat through the discovery and detection of any network communication. One of many network analyzers, this application arguably does the most comprehensive job of seeing and recognizing everything that goes by its sensor.
http://digitalnomad.suck-o.net/DNR/red/wiresharktut.pdf
HostAP
HostAP is really nothing more than a firmware for Prism cards to act as an access point in any environment. With multiple scanning, broadcasting, and management options, HostAP can lure disconnected clients into a connection with the HostAP user’s computer and engage into whatever activities suitable to that situation. This is a very common tool used with growing compatibility where it will be ubiquitous with any Open Source OS in the near future.
FakeAP
FakeAP can generate thousands of counterfeit 802.11b access points.
(ww.blackalchemy.to/project/fakeap)Black Alchemy's Fake AP generates thousands of counterfeit 802.11b access points. Hide in plain sight amongst Fake AP's cacophony of beacon frames. As part of a honeypot or as an instrument of your site security plan, Fake AP confuses Wardrivers, NetStumblers, Script Kiddies, and other undesirables. Fake AP runs on Linux (tested on RedHat 7.3)
Dweputils
Dweputils is not one application but a set of applications that together comprise a larger threat to wireless networks of any character. Dweputils is a set of utilities that can completely inspect and lock-down any WEP network. Dwepdump is a packet-gathering tool, which provides the ability to collect WEP encrypted packets. Dwepcrack then gives you the power to deduce WEP keys with a variety of frequently employed technique. Finally dwepkeygen, a 40-bit key generator, can creates keys that aren't susceptible to the Tim Newsham 221 attack with a variable length seed.
NetStumbler
This is the primary tool available for Windows users to detect 802.11 networks. It does not have any cracking tools that are inherent in the software package but can be used in conjunction with numerous other tools to find and hack a wireless network. NetStumbler is the only wifi locator app that has a audible alert sound that lets the wardriver know he has a 'hit'.
StumbVerter
(
www.sonar-security.com/sv.html) This is a tool that reads NetStumbler's collected data files and presents street maps showing the logged WAPs as icons, whose color and shape indicating WEP mode and signal strength.
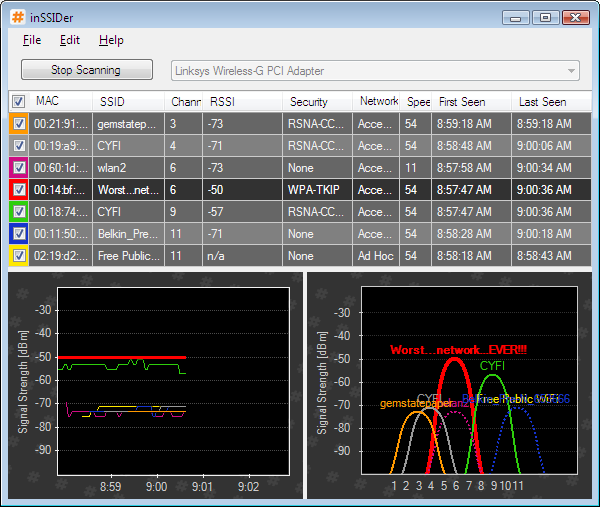
InSSIDer
This is a graphical 'Netstumbler' like program for windows. You can get it at metageek.net and it is freeware.
 WifiHopper
WifiHopper
WiFi Hopper is a WLAN utility that combines the features of a Network Discovery and Site Survey tool with a Connection Manager. WiFi Hopper can connect to unsecured, WEP, WPA-PSK and WPA2-PSK networks directly from within the application. Only 32-bit Windows Vista, Windows 2003, Windows XP SP2 (or higher) and Windows 2000 SP4 (or higher) are supported. htp://wifihopper.com
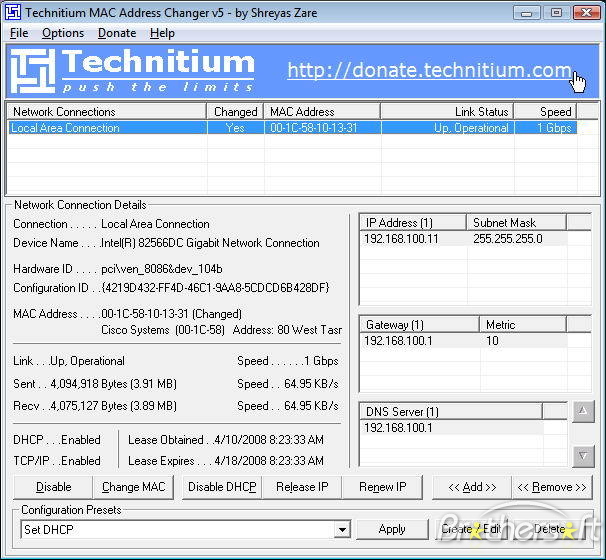
Technitium MAC Address Changer
Technitium MAC Address Changer allows you to change Media Access Control (MAC) Address of your Network Interface Card (NIC) irrespective to your NIC manufacturer or its driver. It has a very simple user interface and provides ample information regarding each NIC in the machine.
http://tmac.technitium.com/tmac/index.html
 OpenWrt
OpenWrt
OpenWrt is a Linux-based firmware program for embedded devices such as residential gateways. Support was originally limited to the Linksys WRT54G series, but has since been expanded to include other chipsets, manufacturers and device types, including Netgear, D-Link, Asus routers and many others, including the Openmoko mobile phones. The most popular routers seem to be the Linksys WRT54G series and the Asus WL-500g. OpenWrt primarily uses a command-line interface, but also features an optional web-based GUI interface. This is ideal for Warkitting.
THC-RUT
Also referred to as the “aRe yoU There” network tool, THC-RUT, combines detection, spoofing, masking, and cracking into the same tool. Many see it as the, “first knife used on a foreign network” boasting its brute force all-in-one capabilities. Resources in the tool included spoofing Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), Reverse Address Resolution Protocol (RARP), and Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP) requests. (
www.thc.org)
BackTrack
BackTrack focuses its central idea on the needs of Penetration testers. The inclusion of Live CD and Live USB functionality enables any user to just insert their respective data medium and boot up a Linux-type OS. Direct hard disk installations (2.7 GB uncompressed) can also be completed within the Live CD (700 MB compressed) environment through the basic graphical installation wizard with no restart subsequent to installation. Backtrack is not just linux, it is a suite of tools for enumeration, exploitation, sniffing, injecting - and for both wireless and cabled networks.
 Hotspotter
Hotspotter
Hotspotter is another rouge access point tool that can mimic any access point, dupe users to connecting, and authenticate with the hacker’s tool. This, again, is done with a deauthenticate frame sent to a MS Windows XP user’s computer that would cause the victim’s wireless connection to be switched to a non-preferred connection, AKA a rouge AP. This sort of trick is a passive approach that seeks to identify the probe frame sent by any Windows XP machine looking for its preferred network containing exploitable information.
ASLEAP
LEAP stand for Lightweight Extensible Authentication Protocol, which is intellectual property of Cisco Systems, Inc. This is a broadly used protocol for authentication on Cisco Access points with inherent weaknesses. ASLEAP is able to use hashing algorithms to create brute force attacks to recover passwords, and actively deauthenticate users from the AP making them reauthenticate quickly to expedite the process of hacking. This is another tool in the arsenal of hackers with an ever-shrinking learning curve. (
www.thc.org)
IKECrack
IKECrack is an open source IKE/IPSec authentication crack tool. It uses brute force dictionary based attacks searching for password and key combinations to Pre-Shared-Key (PSK) authentication networks. With repetitive attempts at authentication with random passphrases or keys this crack tool undermines the latest WiFi security protocol.
WirelessKeyView
www.nirsoft.net WirelessKeyView recovers all wireless network keys (WEP/WPA) stored in your computer by the 'Wireless Zero Configuration' service of Windows XP or by the 'WLAN AutoConfig' service of Windows Vista. It allows you to easily save all keys to text/html/xml file, or copy a single key to the clipboard. Physical or remote access required.
WifiSlax
Wifislax is a Slackware-based live CD containing a variety of security and forensics tools. The distribution's main claim to fame is the integration of various unofficial network drivers into the Linux kernel, thus providing out-of-the-box support for a large number of wired and wireless network cards.
http://www.wifislax.com/
WinDump
WinDump is the Windows version of tcpdump, the command line network analyzer for UNIX. WinDump is fully compatible with tcpdump and can be used to watch, diagnose and save to disk network traffic according to various complex rules. It can run under Windows 95, 98, ME, NT, 2000, XP, 2003 and Vista.
http://www.winpcap.org/windump/default.htm
--
Defense against wifi tools
Just as it’s important to know how to utilize the aforementioned tools, it is important to know best practices on how to secure your Wireless Network Against these tools.
NetStumbler – Do not broadcast your SSID. Ensure your WLAN is protected by using advanced Authentication and Encryption.
Kismet – There’s really nothing you can do to stop Kismet from finding your WLAN, so ensure your WLAN is protected by using advanced Authentication and Encryption
Airsnort – Use a 128-bit, not a 40-bit WEP encryption key. This would take longer to crack. If your equipment supports it, use WPA or WPA2 instead of WEP (may require firmware or software update).
Cowpatty – Use a long and complex WPA Pre-Shared Key. This type of key would have less of a chance of residing in a dictionary file that would be used to try and guess your key and/or would take longer. If in a corporate scenario, don’t use WPA with Pre-Shared Key, use a good EAP type to protect the authentication and limit the amount of incorrect guesses that would take place before the account is locked-out. If using certificate-like functionality, it could also validate the remote system trying to gain access to the WLAN and not allow a rogue system access.
ASLeap – Use long and complex credentials, or better yet, switch to EAP-FAST or a different EAP type.
Ethereal/Wireshark – Use encryption, so that anything sniffed would be difficult or nearly impossible to break. WPA2, which uses AES, is essentially unrealistic to break by a normal hacker. Even WEP will encrypt the data. When in a Public Wireless Hotspot (which generally do not offer encryption), use application layer encryption, like Simplite to encrypt your IM sessions, or use SSL. For corporate users, use IPSec VPN with split-tunneling disabled. This will force all traffic leaving the machine through an encrypted tunnel that would be encrypted with DES, 3DES or AES.
--
References
hawkingtech.com
Wardriver tools list - Daniel V. Hoffman, CISSP, CWNA
htp://forums.remote-exploit.org/showthread.php?t=7127
htp://
www.suck-o.com/modules.php?name=Forums& ... pic&t=4230
htp://digitalnomad.suck-o.net/DNR/red/warkit.pdf
Fingerprinting 802.11 Devices
http://digitalnomad.suck-o.net/DNR/red/ ... finger.pdf
A Guide to Wardriving and Detecting Wardrivers
http://digitalnomad.suck-o.net/DNR/red/ ... rivers.pdf
htp://wirelessdefence.org/Contents/AircrackMain.htm
htp://
www.iss.net/security_center/advice/Coun ... efault.htm
htp://i.technet.microsoft.com
htp://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/BackTrack
/
www.3com.com/other/pdfs/products/en_US/101900.pdf
--
WarDriving with DNR - 2009 edition
DNR (Writer for suck-o.com)
Digital Mercenary


Joined: Feb 25, 2006
Posts: 3699
Location: Michigan USA
--